Artificial Photosynthesis
Catalyzing Sustainable Electrosynthesis
We develop catalysts for sustainable electrosynthesis to address climate change and rising global energy demands. Inspired by natural photosynthesis, which produces the value-added products needed to sustain life from light, water, and carbon dioxide, we use biological design principles to create synthetic molecular electrocatalysts for carbon dioxide capture and conversion as well as nitrogen/phosphorus cycling.
Related Publications
Reviews
-
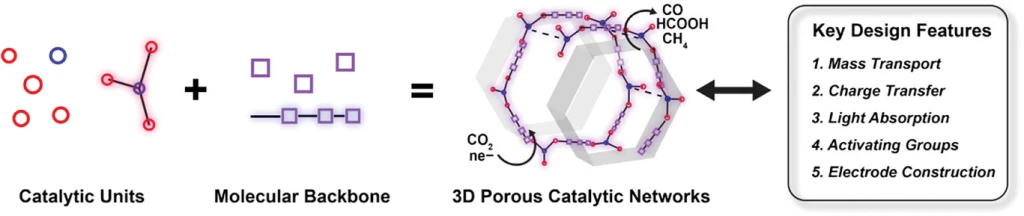
Porosity as a Design Element for Developing Catalytic Molecular Materials for Electrochemical and Photochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction
-

Hybrid Catalysts for Artificial Photosynthesis: Merging Approaches from Molecular, Materials, and Biological Catalysis
-

Metal-Polypyridyl Catalysts for Electro- and Photochemical Reduction of Water to Hydrogen
-

Complexes of earth-abundant metals for catalytic electrochemical hydrogen generation under aqueous conditions
Molecular Catalysis
-

Multifunctional Charge and Hydrogen-Bond Effects of Second-Sphere Imidazolium Pendants Promote Capture and Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 in Water Catalyzed by Iron Porphyrins
-

Exchange Coupling Determines Metal-Dependent Efficiency for Iron- and Cobalt-Catalyzed Photochemical CO2 Reduction
-

Templating Bicarbonate in the Second Coordination Sphere Enhances Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Catalyzed by Iron Porphyrins
-

Metal–Ligand Cooperativity via Exchange Coupling Promotes Iron- Catalyzed Electrochemical CO2 Reduction at Low Overpotentials
-

Positional effects of second-sphere amide pendants on electrochemical CO2 reduction catalyzed by iron porphyrins
-

Bioinspired design of redox-active ligands for multielectron catalysis: effects of positioning pyrazine reservoirs on cobalt for electro- and photocatalytic generation of hydrogen from water
-

Visible-Light Photoredox Catalysis: Selective Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Carbon Monoxide by a Nickel N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Isoquinoline Complex
-

Molecular Cobalt Pentapyridine Catalysts for Generating Hydrogen from Water
-

A Molecular Molybdenum-Oxo Catalyst for Generating Hydrogen from Water
Bioinorganic, Organometallic, and Supramolecular Hybrids
-
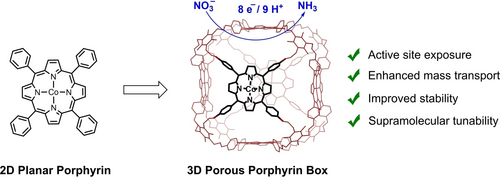
Supramolecular Enhancement of Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction Catalyzed by Cobalt Porphyrin Organic Cages for Ammonia Electrosynthesis in Water
-
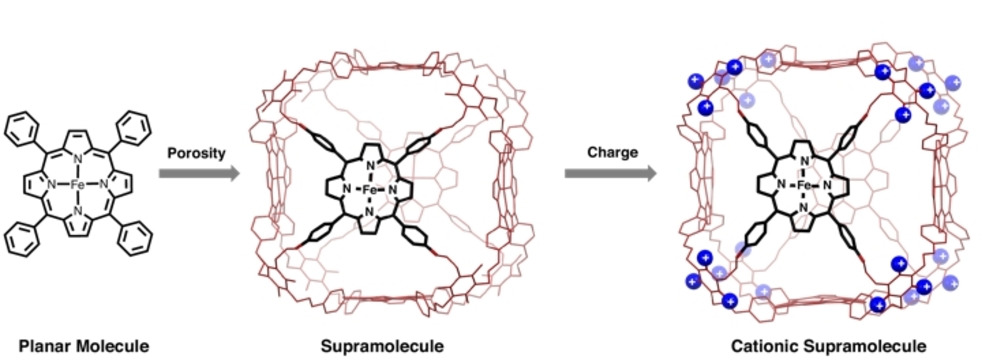
Synergistic Porosity and Charge Effects in a Supramolecular Porphyrin Cage Promote Efficient Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction
-

Supramolecular Tuning Enables Selective Oxygen Reduction Catalyzed by Cobalt Porphyrins for Direct Electrosynthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide
-

Iron Porphyrins Embedded into a Supramolecular Porous Organic Cage for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction in Water
-

Chelating N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands Enable Tuning of Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to Formate and Carbon Monoxide through Surface Organometallic Chemistry
-

Supramolecular Porphyrin Cages Assembled at Molecular–Materials Interfaces for Electrocatalytic CO Reduction
-

A Molecular Surface Functionalization Approach to Tuning Nanoparticle Electrocatalysts for Carbon Dioxide Reduction
-

Hybrid bioinorganic approach to solar-to-chemical conversion
-

Covalent organic frameworks comprising cobalt porphyrins for catalytic CO2 reduction in water
